Blockchain Storage
Learn about IPFS(InterPlanetary File System) and how we store data on blockchain.
To understand the storage system on blockchain we need to first understand what we store in the blockchain. My previous Blockchain Structure explains this.
Introduction to blockchain storage
The blockchain contains some data, such as transactions or other information, and a unique code, called a hash, hash is generated based on the contents of the block. The hash is used to identify the block and ensure its integrity.
One of the popular blockchains is Ethereum, it can store data, including images, but it is not an ideal storage solution for large files due to the limited storage capacity and high cost of storing data on the blockchain. Whenever the data size of the Ethereum chain reaches 1 Tb pruned happens, Pruning is the process of erasing older data to save disk space.
However, there are some ways to store files on the Ethereum network. One standard method is to use IPFS (InterPlanetary File System), a decentralized storage system that allows for the efficient and secure distribution of files. IPFS can be used to store files and other large documents off-chain, while the file hash is stored on the Ethereum blockchain, ensuring that the data is tamper-proof and publicly verifiable.
Traditional storage vs blockchain storage
Traditional storage systems rely on a centralized server or data center to store and manage data. This centralized approach makes the data vulnerable to attacks, data breaches, and censorship, as well as more costly to manage and maintain. Centralized systems also require users to trust the centralized authority to manage their data, which can lead to issues with privacy, security, and control. Suppose a company has a data server, which is located in XYZ location if there is a natural disaster, then there is a risk of data loss.
On the other hand, blockchain storage uses a decentralized and distributed network of nodes to store and share data. This makes the data more secure, transparent, auditable, and more efficient and cost-effective to manage. Users have more control over their data, as they can store it themselves or choose who to share it with, without relying on a centralized authority.
Decentralized storage and its benefits
Decentralized storage refers to the use of a network of nodes to store and share data in a distributed and decentralized manner. This approach has several benefits, including:
Increased security: Decentralized storage makes it more difficult for hackers or attackers to access or compromise the data, as there is no single point of failure or vulnerability.
Increased privacy: Decentralized storage allows users to control and manage their data, without having to rely on third-party service providers that may collect or share their data.
Reduced costs: Decentralized storage can be more cost-effective than traditional storage systems, as it eliminates the need for centralized servers or data centers, as well as the associated costs of managing and maintaining them.
Distributed ledger technology
Distributed ledger technology (DLT) is a type of database that is shared across a network of nodes and updated through a consensus mechanism. DLT is a fundamental component of blockchain technology, as it allows for the secure and transparent storage and transfer of data. In blockchain storage, DLT is used to store and manage the data in a decentralized and distributed manner, ensuring its integrity and immutability.
IPFS (InterPlanetary File System)
IPFS (InterPlanetary File System) is a distributed file system that provides a decentralized method of storing and accessing files on the internet. It was created to address some of the limitations of traditional centralized file storage systems, such as slow download speeds, high bandwidth costs, and the risk of data loss or censorship.
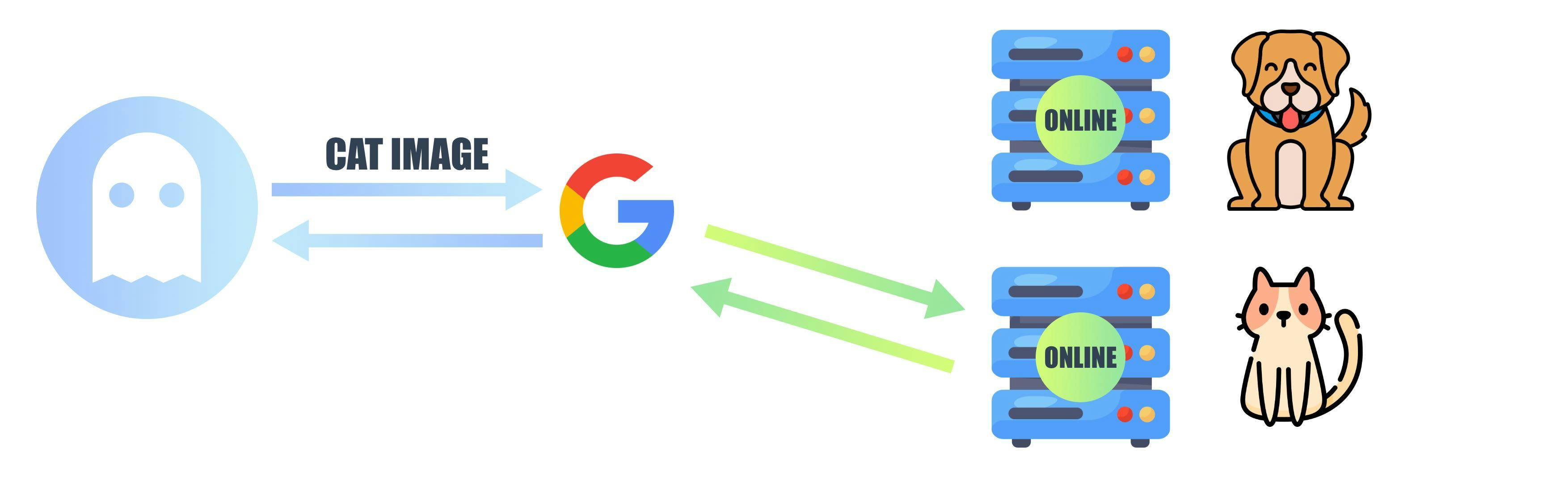
Whenever you search for something on the internet like a picture of a cat 🐈, the search engine would provide you with a link, https://website.com/cat.jpg this means there is a computer in the world in which the picture of the cat is stored and we are accessing it using the link. This is called location-based addressing. Suppose the computer is off then the cat image is also not available. There may be some people who have already downloaded the image of the cat but we can't get it from that person.
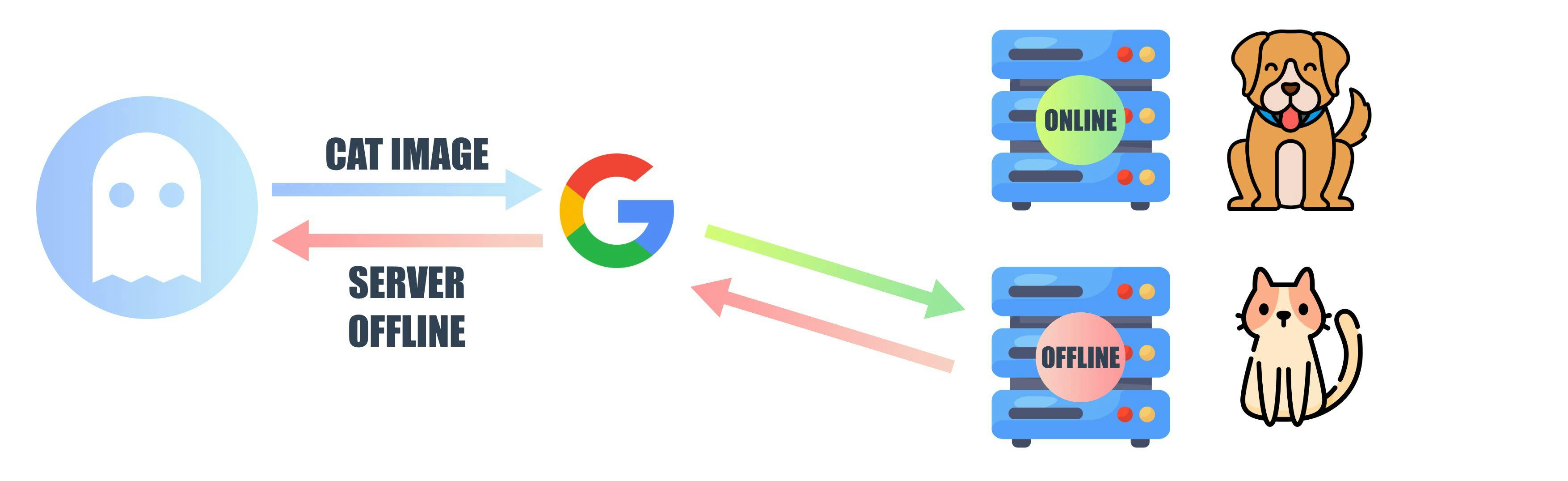
Content-Base Addressing
IPFS uses Content Base Addressing instead of location, so what does it mean? Instead of locating the file with its address, IPFS located the file with its content. In the article Cryptography, we have seen how each file has a unique hash, IPFS uses this hash method to locate files.
Suppose some people are connected to an IPFS network and one person has a cat image stored in his computer and other people request a cat image in that network. The person who has the image will give it.
Give me the picture with key nsfeH7jn89N
Another person who has requested the cat image will ask for the image with a hash, nsfeH7jn89N, after the person receives the file he or she can compare the hash and verify if somebody has tampered with the data. One of the other advantages is when many people publish the same file in the IPFS, the file is created once as other files have the same hash, which makes the network very efficient.
Storage of data
IPFS stores files as an object, which contains Data and Links, Each object can store up to 256kb of data and each object can store links to other objects. A simple Hello World text is less than 256kb and can store in a single IPFS object. To store data of more than 256kb the data is split into more than one IPFS object and each object store data up to 256kb, after that, the system creates an empty IPFS object which links to the other split objects.
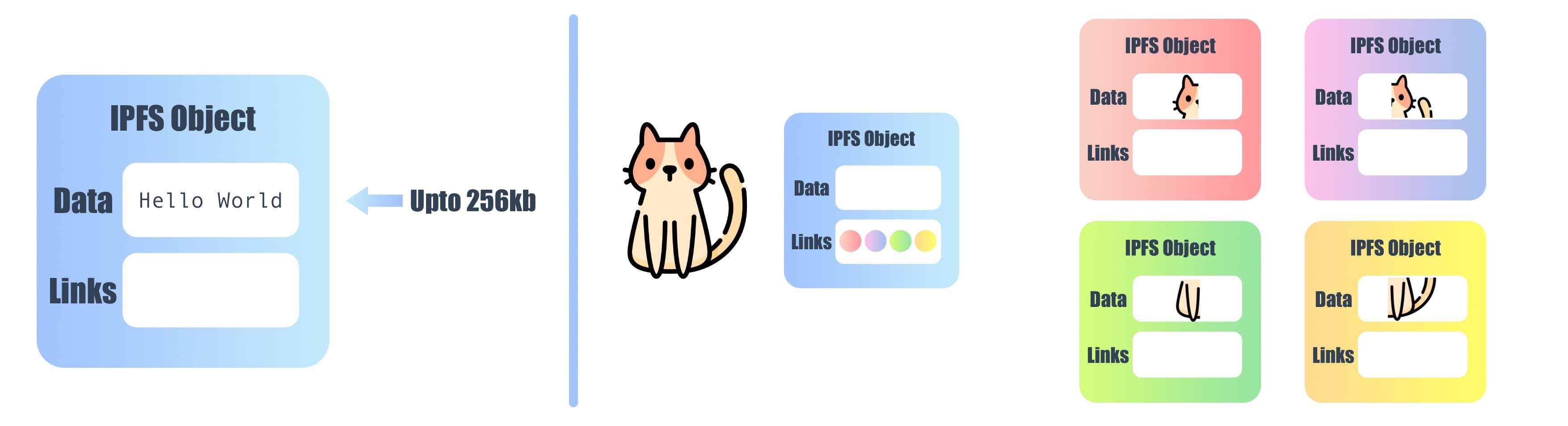
Once the data is added to the IPFS it can't be changed and the data become immutable because it uses a content base address, but how do we change our data if we need to? We can use versioning.
Versioning
IPFS support the versioning of file just like git. Whenever we publish a file in the network, the system makes a commit object of that file. A commit object has two things Parent and Object. The parent stores the previous commit of the file and the Object points to the current version of the file.
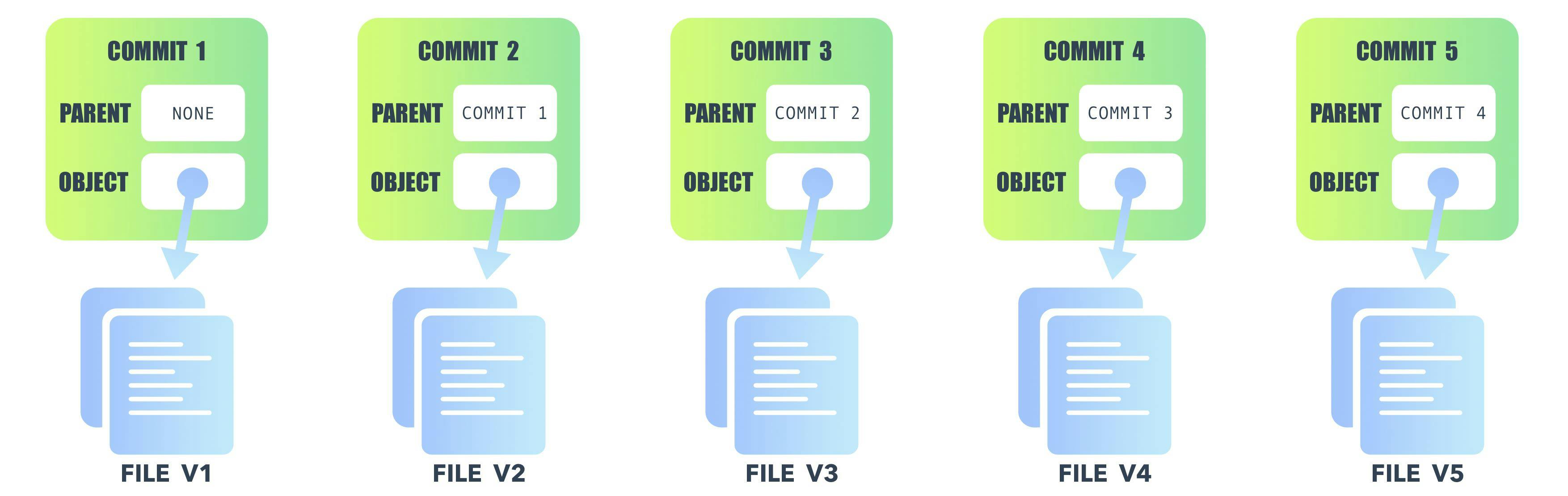
IPFS makes sure that your file and its entire history are accessible to other nodes on the network.
What's on the next article?
Next, we will see what is Mining and Incentive Models.


