Blockchain Structure
Understand how a blockchain work and what makes a blockchain.
understand how a blockchain work and what makes a blockchain.
Today we are going to see how a blockchain work. In our previous article, we have seen some of the terminologies related to it, if you have not read it you should go through it "What is Blockchain?".
This article will be divided into 6 parts :
SHA256 Hash
Block
Blockchain
Distributed Blockchain
Tokens or Transaction
Coinbase Transactions
SHA256 Hash
First, let us see what is SHA256 HASH I will explain it in detail later on. Here is a short description, SHA256 Hash is a function that takes an input and returns a fixed 256-character of string which is called Hash, and each Hash is unique for different data.
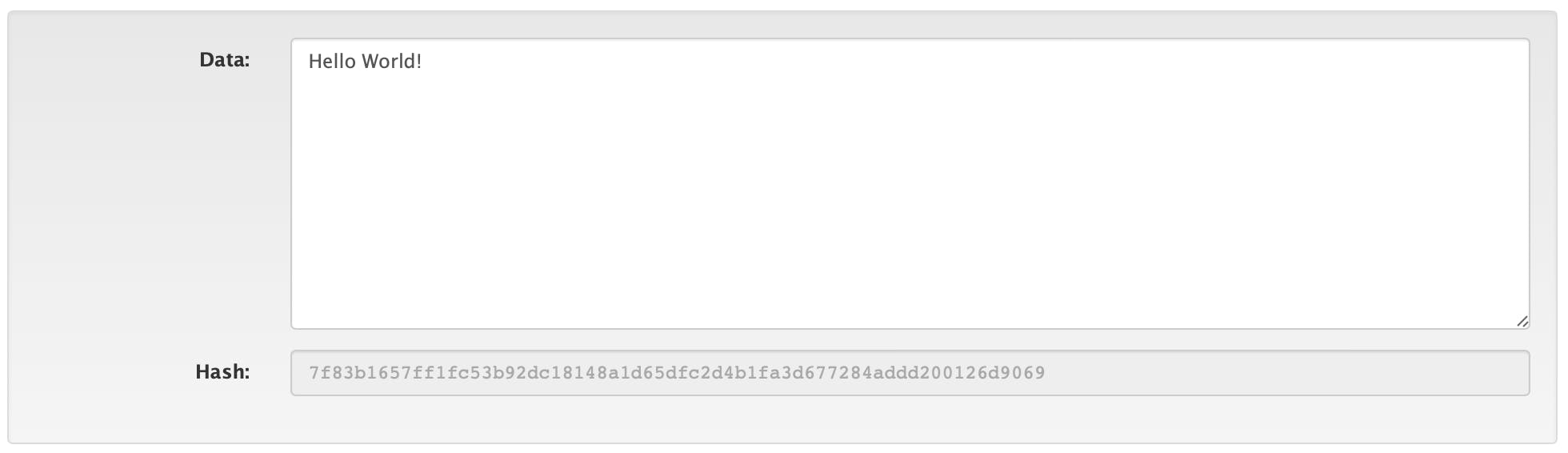

Here you can see both the hash are different as the first letter 'H' is capitalized in the first input and the 'h' small letter in the second although the other characters are the same.
Later in this series, there will be an article on Cryptography here I will explain this topic thoroughly.
Block
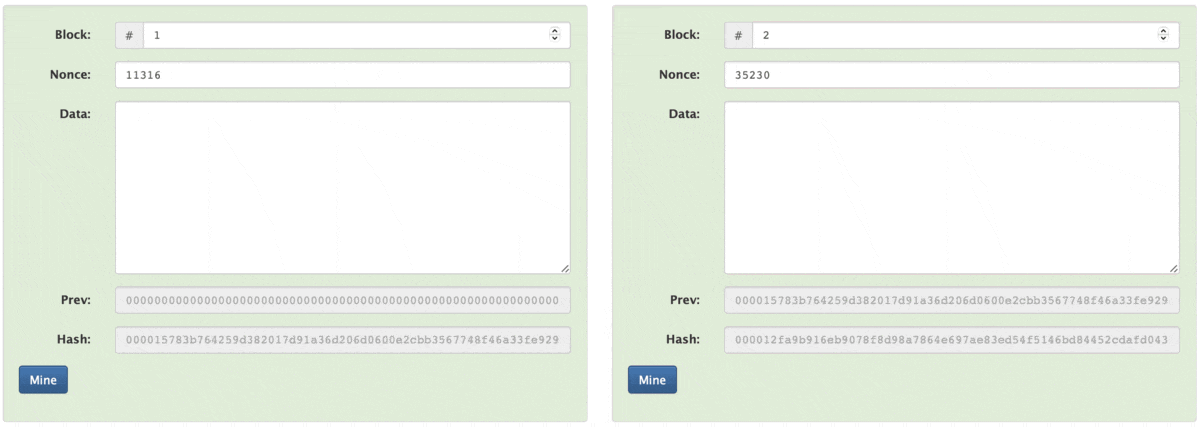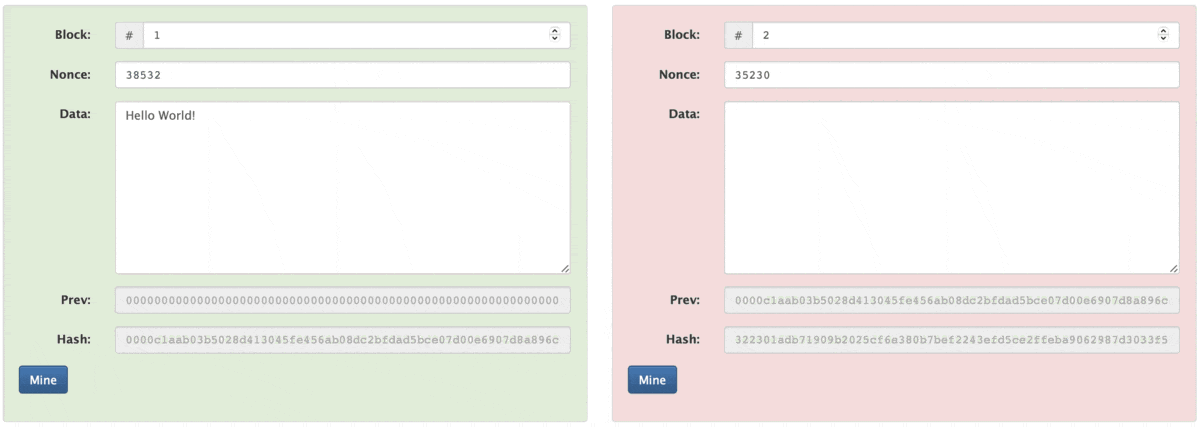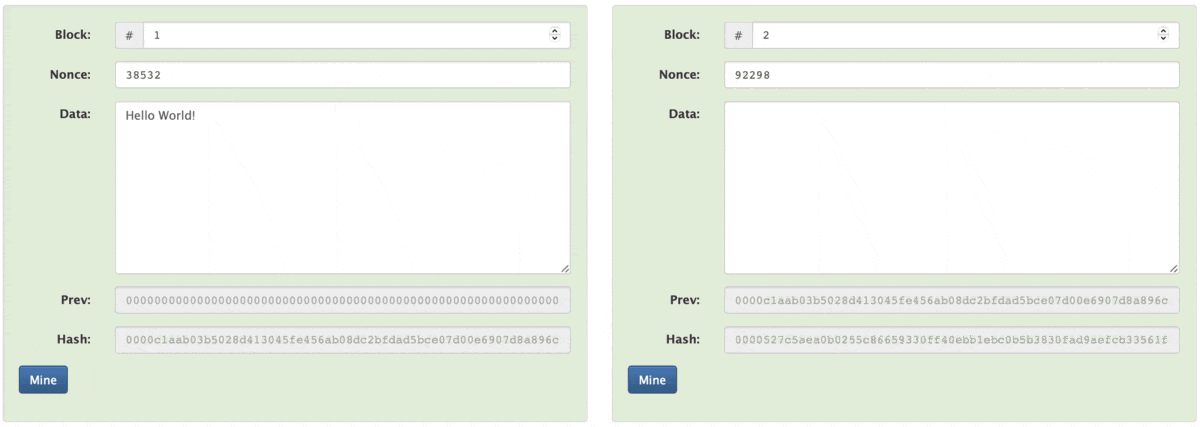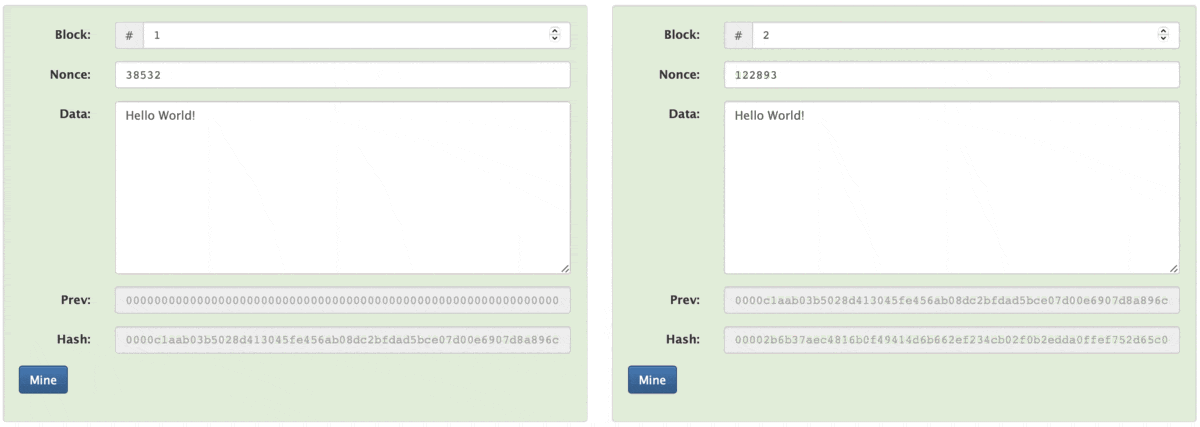
Now we will see what is a block, In simple in a block we have a block number, nonce, data, and hash. Here you can see the new word Nonce, now you are thinking what is a nonce? Nonce is a random number that is used in the proof-of-work mechanism to validate the block and add it to the blockchain.

To generate a signed hash that can be added to a blockchain, the input data, such as "Hello World!", must first be hashed using a cryptographic hash function. The resulting unsigned hash, such as "7f83b......d9069", is not suitable for this purpose as it does not meet the specific criteria required for a block hash in a blockchain.
To produce a signed hash, a miner employs a brute-force approach to find a nonce value that, when combined with the block number and data, generates a hash that meets the necessary criteria. This often involves starting with a nonce of 1 and incrementing it until a value is found that produces a hash that begins with the desired number of zeros (e.g. "0000"). The combination of the block number, nonce, and data results in the final block hash, which can then be added to the blockchain.

Blockchain
Till now we have seen what is a block and what is a SHA256 Hash now we will see what is blockchain but before that, have you seen one more section above the Hash.
Blockchain is a series of blocks that contain data and which is connected to the previous block with a cryptographic hash. In a block, we have a previous hash data field that stores the hash of the previous block.
Previous Hash stores the hash of the previous block so we can verify the previous block, It forms a chain-like structure as each block is connected to the previous block. In the first article, I talk about the Genius block under the Ledger section, here you can see the first block (which is block number 1) has Prev equal to "0000....000" as the first block does not have a block before it, so the previous hash will be NULL or "000....000".
Whenever a new block is added to a blockchain it takes the hash of the previous block and stores it, Check block 1 Hash and block 2 Prev, the hash you will find is the same.


Whenever we try to temper the previous block's data, the blocks will be invalid. So, we need to mine the blocks one by one.
Distributed Blockchain
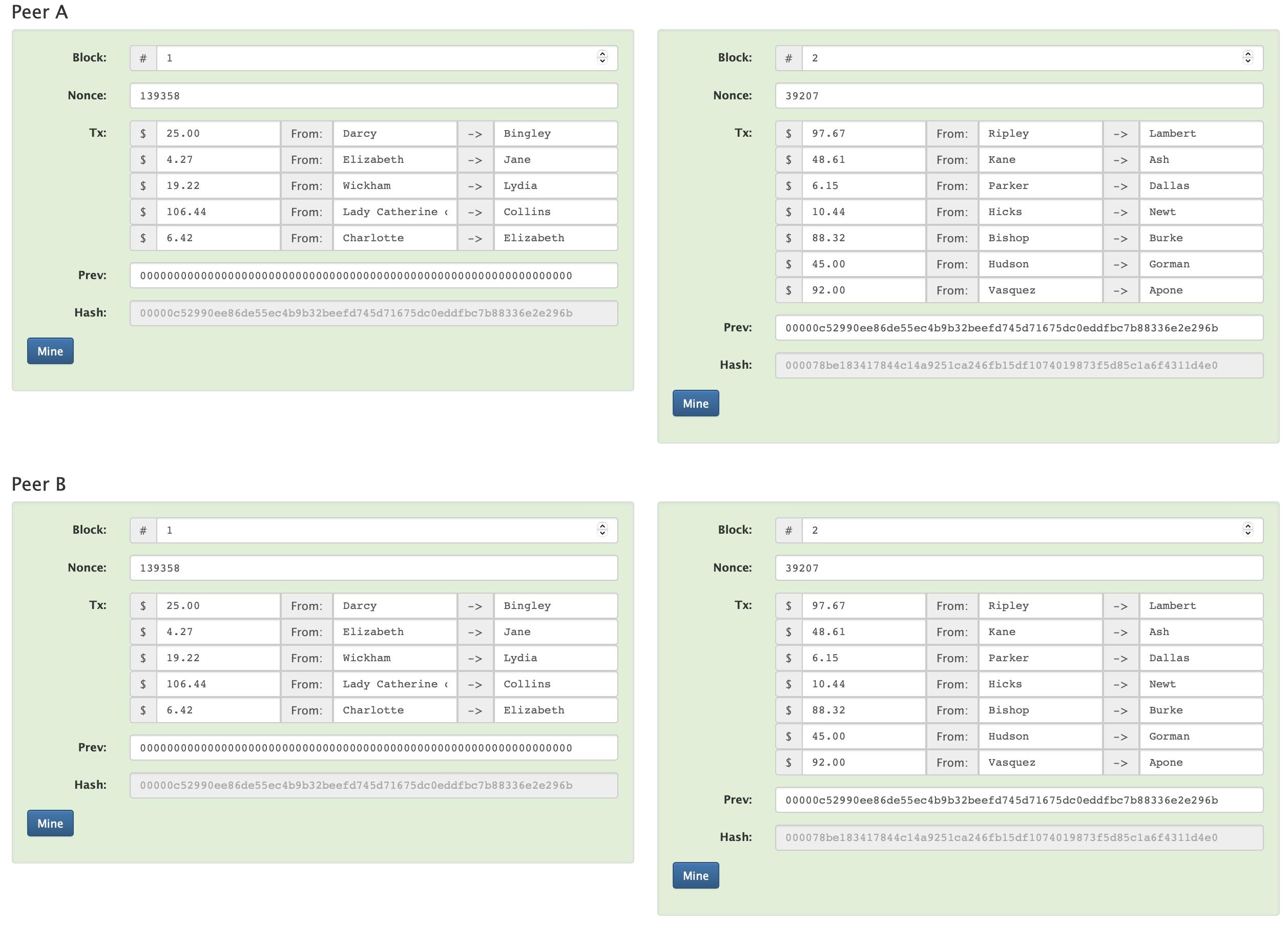
Now further extending the knowledge of blockchain, we will see what distributed blockchain is. It is a system, where a ledger is replicated and distributed to each node around the world.
Blockchain nodes are the moderators that build the infrastructure of a decentralized network.


A decentralized ledger that is maintained by a network of computers is known as a distributed blockchain. There is no centralized authority or single point of control in a distributed blockchain. Instead, each node in the network keeps a copy of the ledger and uses consensus techniques to verify transactions. As it becomes more challenging for any one node or set of nodes to influence the ledger, this design enables enhanced security, transparency, and reliability.
Tokens or Transaction
Whenever we add a block there is some data but before the data doesn't mean anything or it was useless, to make the blockchain valuable or worth something we can store transactions.
Coinbase Transactions
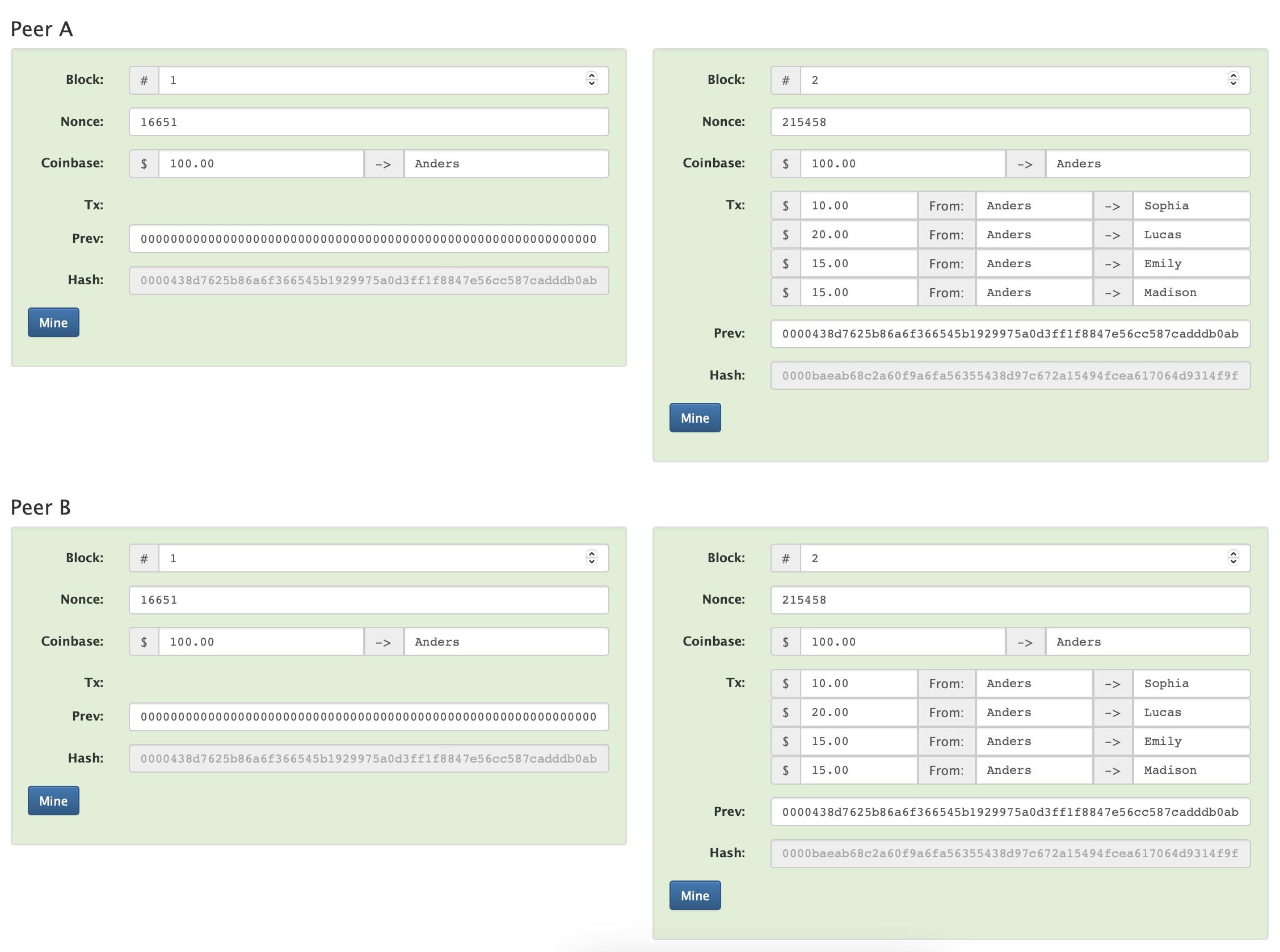
In the blockchain, whenever a new block is mined by the miner he is rewarded with a coin in his account, this coinbase transaction doesn't have a previous reference.
Let us think the Genius block is mined by Anders so he is rewarded with 100 coins in his account now he can give these coins to other accounts in the blockchain, these coins do not have a previous reference but when Sophia tries to send coins to another account she needs to have coins in her account she can get this coin from Anders or when the blockchain was created the creates can distribute this coin.
What's on the next article?
Next, we will see what is decentralization and compare it with our current internet.